Sing Musical Theatre
Singing Technique

Better, Faster Stronger
Build the Voice That Books the Role
Whether you’re belting a showstopper or floating a legit ballad, great singing starts with great technique. These core concepts break down the how and why of vocal mastery—so you can sing with confidence, power, and emotion every time you step on stage.
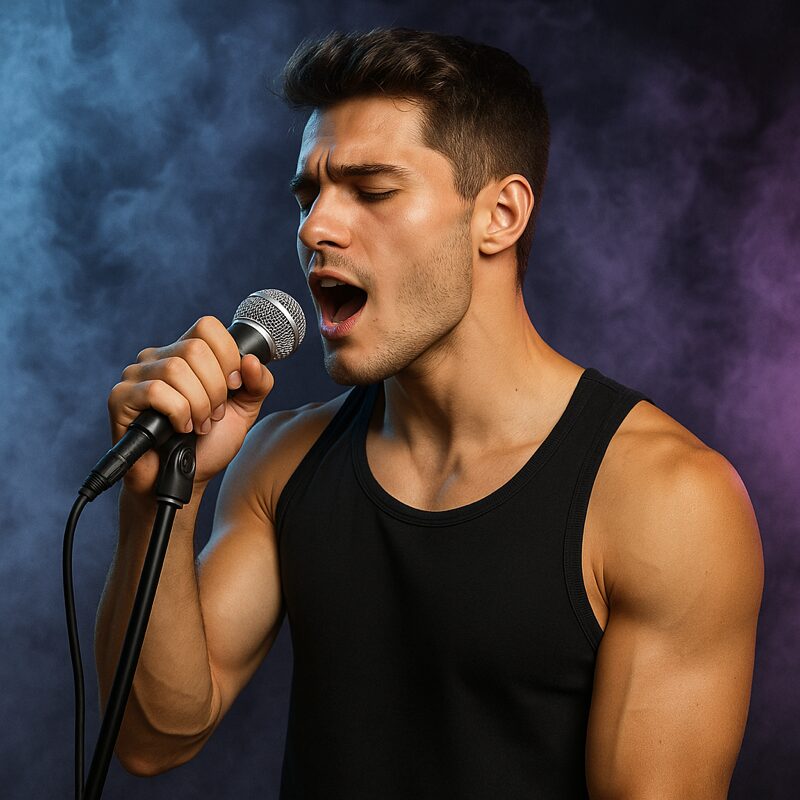

Sing Musical Theatre
Technique Concepts
What do you want to learn today?
Breathing / Support
Sing Longer, Stronger: The Power of Breath Support
Placement
Where Does the Sound Go? Discovering Vocal Placement That Works
Vocal Health
Sing Smarter, Stay Strong: Daily Habits That Protect Your Voice
Pitch
u003cpu003eFusce sagittis et nisi in feugiatu003c/pu003e
Vocal WarmUps
u003cpu003eFusce sagittis et nisi in feugiatu003c/pu003e
Posture
u003cpu003eFusce sagittis et nisi in feugiatu003c/pu003e
Resonance
u003cpu003eFusce sagittis et nisi in feugiatu003c/pu003e
Vowel Modification
u003cpu003eFusce sagittis et nisi in feugiatu003c/pu003e

Singing Cool-Downs
u003cpu003eFusce sagittis et nisi in feugiatu003c/pu003e

Blending Registers
Master Your Mix: Blending Chest and Head Like a Pro

Dynamic Control
u003cpu003eFusce sagittis et nisi in feugiatu003c/pu003e

Head Voice
u003cpu003eFusce sagittis et nisi in feugiatu003c/pu003e
Basics of Vocal Technique: Core Foundations for Singers
A beautiful, healthy singing voice doesn’t happen by accident. It’s built on solid technical foundations that let you sing expressively without strain. This guide covers the core concepts that every singer—beginner to professional—should master.
Posture & Alignment
Good posture sets the stage for every aspect of vocal technique. Keep the spine long, shoulders relaxed, and weight evenly balanced over both feet. Your head should float above the spine—not jut forward or tilt back.
Breathing & Support
Breath is your fuel. Inhalations should expand low into the ribs and back, avoiding shoulder lift. Exhalation is controlled by engaging the diaphragm and lower abdominal muscles, maintaining steady airflow.
- Practice silent, low breaths to prepare for phrasing.
- Use long, sustained tones to train control.
- Coordinate breath release with the onset of sound.
Resonance & Placement
Resonance shapes your tone and projection. Adjusting the soft palate, tongue position, and pharyngeal space changes the color of your sound. Aim for a balanced resonance that combines warmth and clarity.
Tone Production
Tone is created when the vocal folds vibrate efficiently with minimal tension. Keep the throat open and allow air to flow freely. Avoid pushing for volume—rely on resonance and breath support instead.
Diction & Articulation
Clear diction ensures your lyrics are understood without compromising tone. Consonants should be precise but not forced, and vowels should remain pure unless modified for pitch or resonance.
Registers & Transitions
Most singers navigate chest, mix, and head registers. Smooth transitions (“passaggio”) require balanced breath and vowel modification. Train all registers so none feels weak or disconnected.
Dynamics & Control
Dynamic contrast adds expression. Practice crescendo and decrescendo on sustained notes to train control without tension. Link changes in volume to musical and emotional intent.
Healthy Practice Habits
- Warm up gently before demanding singing.
- Rest your voice if you feel strain or fatigue.
- Hydrate regularly and avoid excessive caffeine or alcohol.
- End sessions with light, comfortable exercises.
Vocal Technique Checklist
- Posture aligned and relaxed.
- Breathing low and silent.
- Even, supported airflow.
- Balanced resonance (warmth + clarity).
- Clear vowels and crisp consonants.
- Registers connected smoothly.
- Controlled dynamics.
- Healthy warm-up and cooldown.
Common Mistakes & Fixes
- Raised shoulders when breathing: Focus on rib and back expansion.
- Tension in the jaw or tongue: Massage and stretch before singing.
- Forcing volume: Rely on resonance, not pressure.
- Flat or dull tone: Adjust resonance and vowel space.